Topics
M87* One Year Later: Proof of a persistent black hole shadow
Results published in "Astronomy and Astrophysics" and press release issued from EHT on January 18, 2024.
2024.01.18
The Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) Collaboration, in which Prof. Kenji Toma from Tohoku University's Frontier Institute for Interdisciplinary Sciences participates, has released new images of M87*, the supermassive black hole at the center of the galaxy Messier 87, using data from observations taken in April 2018. With the participation of the newly commissioned Greenland Telescope and a dramatically improved recording rate across the array, the 2018 observations give us a view of the source independent from the first observations in 2017. A recent paper published in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics presents new images from the 2018 data that reveal a familiar ring the same size as the one observed in 2017. This bright ring surrounds a deep central depression, “the shadow of the black hole,” as predicted by general relativity. Excitingly, the brightness peak of the ring has shifted by about 30º compared to the images from 2017, which is consistent with our theoretical understanding of variability from turbulent material around black holes.
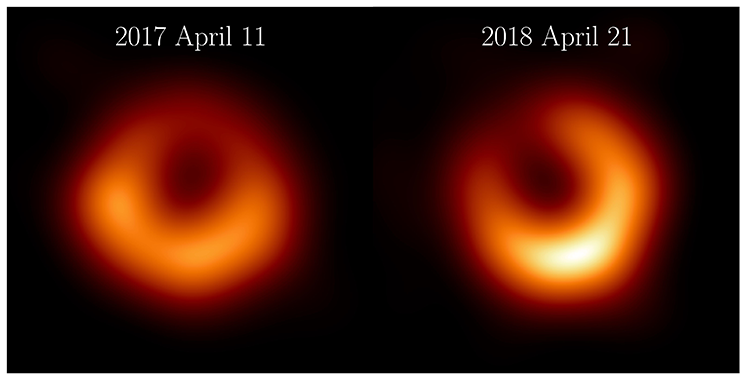
The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration has released new images of M87* from observations taken in April 2018, one year after the first observations in April 2017. The new observations in 2018, which feature the first participation of the Greenland Telescope, reveal a familiar, bright ring of emission of the same size as we found in 2017. This bright ring surrounds a dark central shadow, and the brightest part of the ring in 2018 has shifted by about 30º relative from 2017 to now lie in the 5 o’clock position.
Credit: EHT Collaboration
Credit: EHT Collaboration
Please see the press release from EHT-Japan for details.
Publication Details
Title: The persistent shadow of the supermassive black hole of M87. I. Observations, calibration, imaging, and analysis
Authors: Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration et al.
Journal: Astronomy and Astrophysics
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202347932
URL: https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202347932
Title: The persistent shadow of the supermassive black hole of M87. I. Observations, calibration, imaging, and analysis
Authors: Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration et al.
Journal: Astronomy and Astrophysics
DOI: 10.1051/0004-6361/202347932
URL: https://doi.org/10.1051/0004-6361/202347932